Tinned copper strip is a metal material with a layer of tin on the surface of the copper strip. The production process of tinned copper strip is divided into three steps: pre-treatment, tin plating and post-treatment.
According to the different tin plating methods, it can be divided into electroplating and hot-dip plating. There are differences between electroplated tinned copper strip and hot-dip tinned copper strip in many aspects.
I. Process principle
1) Electroplating tinning: It uses the principle of electrolysis to use the copper strip as the cathode and tin as the anode. In the electroplating solution containing tin ions, the tin ions are reduced and deposited on the surface of the copper strip to form a tin-plated layer through the action of direct current.
2) Hot-dip tinning: It is to immerse the copper strip in molten tin liquid. Under certain temperature and time conditions, the tin liquid reacts physically and chemically with the surface of the copper strip to form a tin layer on the surface of the copper strip.
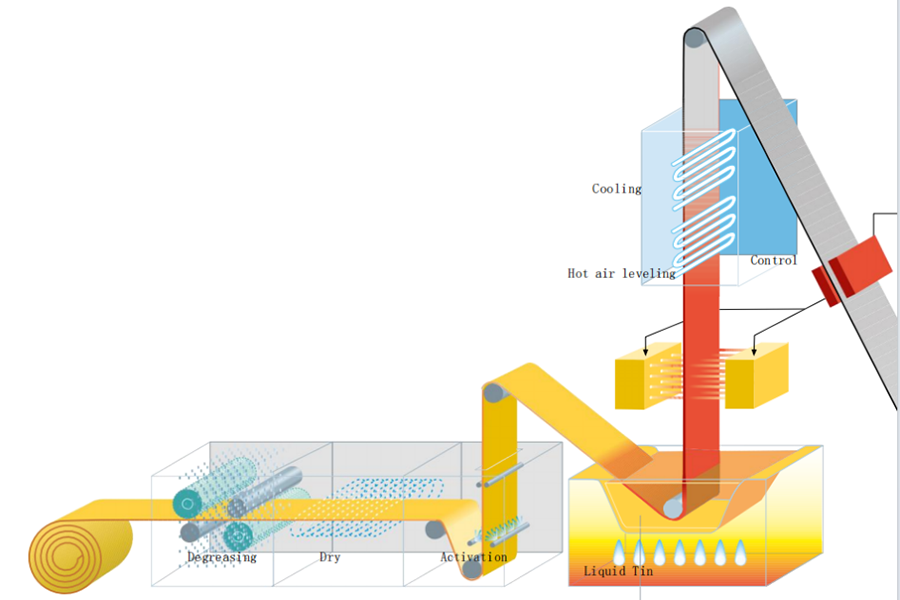
II. Coating characteristics:
1) Coating uniformity
A) Electroplating tinning: The coating uniformity is good, and it can form a uniform and delicate tinning layer on the surface of the copper strip. Especially for copper strips with complex shapes and uneven surfaces, it can also cover well, which is suitable for application scenarios with high requirements for coating uniformity.
B) Hot-dip tinning: The coating uniformity is relatively poor, and uneven coating thickness may occur at the corners and edges of the copper strip. However, for some occasions where the requirements for coating uniformity are not particularly strict, the impact is small.
2) Coating thickness:
A) Electroplating tinning: The coating thickness is relatively thin, generally between a few microns and tens of microns, and can be precisely controlled according to specific needs
B) Hot-dip tinning: The coating thickness is usually thicker, generally between tens of microns and hundreds of microns, which can provide better corrosion resistance and wear resistance for copper strips, but it may not be suitable for some applications with strict restrictions on thickness.
III. Production efficiency
1) Electroplating tin plating: The production process is relatively complex, requiring multiple processes such as pre-treatment, electroplating, and post-treatment. The production speed is relatively slow and is not suitable for large-scale and high-efficiency production. However, for some small-batch and customized production needs, electroplating tin plating has good adaptability.
2) Hot-dip tin plating: The production process is relatively simple. The tin plating process can be completed by immersing the copper strip in the tin liquid. The production speed is fast and can meet the needs of large-scale production.
IV. Bonding strength:
1) Electroplating tin plating: The bonding strength between the coating and the copper strip substrate is strong. This is because the tin ions form chemical bonds with the atoms on the surface of the copper strip under the action of the electric field during the electroplating process, making the coating difficult to fall off5.
2) Hot-dip tin plating: The bonding strength is also good, but in some cases, due to the complex reaction between the tin liquid and the surface of the copper strip during the hot-dip plating process, some tiny pores or defects may appear, affecting the bonding strength. However, after proper post-treatment, the bonding strength of hot-dip tin plating can also meet the requirements of most applications.
V. Corrosion resistance:
1) Electroplating tinning: Due to the thin coating, its corrosion resistance is relatively weak. However, if the electroplating process is properly controlled and appropriate post-treatment, such as passivation, is carried out, the corrosion resistance of the tinned copper strip can also be improved
2) Hot-dip tinning: The coating is thicker, which can provide better corrosion resistance protection for the copper strip. In harsh environmental conditions, such as humid and corrosive gas environments, the corrosion resistance advantage of hot-dip tinned copper strip is more obvious5.
VI. Cost
1) Electroplating tinning: The equipment investment is relatively small, but due to the complex production process, it consumes more electricity and chemical reagents, and has high requirements for the production environment and operators, so the production cost is relatively high.
2) Hot-dip tinning: The equipment investment is large, and high-temperature furnaces and other equipment need to be built, but the production process is simple and the raw material consumption is relatively small, so the unit cost may be relatively low in large-scale production.
Choosing a tinned copper strip suitable for your application scenario requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors such as electrical properties, mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, production process, cost and environmental protection. According to specific needs, weigh the pros and cons of all aspects and choose the most suitable tinned copper strip to ensure the performance and quality of the product.


Post time: Sep-18-2024