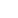
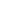Brass strip and leaded brass strip are two common copper alloy strips, the main difference lies in the composition, performance and use.
Ⅰ. Composition
1. Brass is mainly composed of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), with a common ratio of 60-90% copper and 10-40% zinc. Common grades include H62, H68, etc.
2. Leaded brass is a copper-zinc alloy with lead (Pb) added, and the lead content is usually 1-3%. In addition to lead, it may also contain a small amount of other elements, such as iron, nickel or tin, etc. The addition of these elements can further improve the performance of the alloy. Common grades include HPb59-1, HPb63-3, etc.

II. Performance characteristics
1. Mechanical properties
(1) Brass: With the change of zinc content, the mechanical properties are different. When the zinc content does not exceed 32%, the strength and plasticity increase with the increase of zinc content; after the zinc content exceeds 32%, the plasticity drops sharply, and the strength reaches the maximum value near the zinc content of 45%.
(2) Leaded brass: It has good strength, and due to the presence of lead, its wear resistance is better than that of ordinary brass.
2. Processing performance
(1) Brass: It has good plasticity and can withstand hot and cold processing, but it is prone to medium-temperature brittleness during hot processing such as forging, generally between 200-700℃
(2) Leaded brass: It has good strength, and due to the presence of lead, its wear resistance is better than that of ordinary brass. The free state of lead makes it play a friction-reducing role during the friction process, which can effectively reduce wear.
3. Physical and chemical properties
(1) Brass: It has good electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. It corrodes very slowly in the atmosphere and not very fast in pure fresh water, but it corrodes slightly faster in seawater. In water containing certain gases or in specific acid-base environments, the corrosion rate will change.
(2) Leaded brass: Its electrical and thermal conductivity are slightly inferior to brass, but its corrosion resistance is similar to that of brass. In some specific environments, due to the effect of lead, its corrosion resistance may be more prominent.
3. Applications
(1) Brass strips are highly versatile and suitable for a variety of occasions, especially those that require good formability and surface quality.
1)Electronic and electrical industry: connectors, terminals, shielding covers, etc.
2)Architectural decoration: door handles, decorative strips, etc.
3)Machinery manufacturing: gaskets, springs, heat sinks, etc.
4)Daily hardware: zippers, buttons, etc.


(2) Leaded brass strip has excellent cutting performance and is suitable for precision machining, but attention should be paid to the environmental and health issues of lead. In drinking water systems and areas with high environmental protection requirements, it is recommended to use lead-free brass strip.
1)Precision parts: watch parts, gears, valves, etc.
2)Electronic appliances: high-precision connectors, terminals, etc.
3)Automotive industry: fuel system parts, sensor housings, etc.

Post time: Feb-25-2025